ENVIRONMENTAL FACADE
GREEN TECHNOLOGY FOR SUSTAINABILITY
Architectural Practice must embrace design for green buildings, as a vital element in a sustainable society. Many green buildings incorporate curtainwall facades that address the issues of environmental performance and material recycling. Through our experience in Japan’s harsh environmental and climatic conditions, we have pioneered new environmental technologies. While collaborating closely with Architects, we are able to share the knowledge we have gained. We aim to realize their concepts, offering engineered curtainwall solutions that encompass all elements of design, procurement, manufacturing, construction, and maintenance, and at the same time, bring us closer to a sustainable society.
Categories of environmental facade
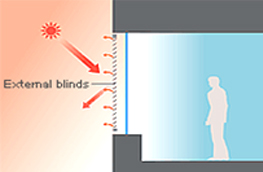
Externalblinds type
- Blinds are located on the exterior side
- The heat from solar gain is absorbed, reflected by blinds on the interior side, and is radiated from the room.
- Solar shading property is high.
- Thermal Insulative property is equal to the glazing.
Solar heat gain coefficient
η=0.05~0.10 η=approx.
Thermal transmittance
U=1.5~2.4 (W/m2 K) U=approx.
*Above values vary with the property of glass and blind
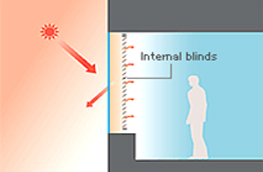
Low-E glass & internalblinds
- Blinds are located on the interior side
- The heat from solar gain is absorbed, reflected by blinds on the interior side and is radiated from the room.
- Solar shading property is low.
- Thermal Insulative property is equal to the glazing.
Solar heat gain coefficient
η=0.30~0.55 η=approx.
Thermal transmittance
U=1.5~2.4 (W/m2 K) U=approx.
*Above values vary with the property of glass and blind
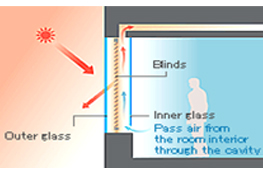
Mechanicallyventilatedtype
- This type uses double-pane glass with blinds between the panes, and pass air from the room interior through the cavity by mechanical ventilation.
- The solar heat absorbed by blinds is removed by mechanical ventilation.
- Solar shading property is high.
- Thermal Insulative property is higher than double-pane glass, due to the airflow in the cavity between the panes. (Varies with the air flow rate).
Solar heat gain coefficient
η=0.15~0.25 η=approx. (when mechanical ventilation is on.)
Thermal transmittance
U=0.5~1.0 (W/m2) K U=approx. (when mechanical ventilation is on.)
*Above values vary with the property of glass and blind and airflow rate
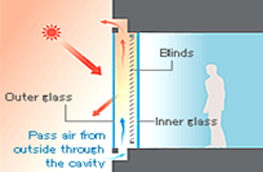
Naturally ventilatedtype
- This type uses double-pane glass with blinds between the panes, and pass air from outside through the cavity by stack effect.
- The solar heat absorbed by blinds is removed by ventilation.
- Solar shading property is high.
- Thermal Insulative property is higher than the inner glazing.
Solar heat gain coefficient
η=0.10~0.20 η=approx.
Thermal transmittance
U=1.5~3.5 (W/m2 K) U=approx.
*Above values vary with the property of glass and blind
Thermal property of facade & thermal load of perimeter zone
The relation between solar shading/ thermal insulation property of facade and thermal load of perimeter zone can be described as below.
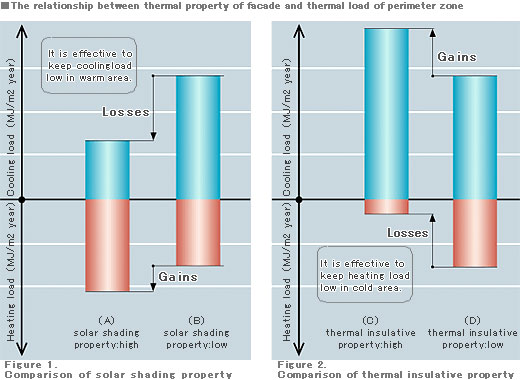
In a warm area such as Tokyo, cooling loads account for the bulk of heating and cooling loads, the superior solar shading property of the facade is effective in reducing thermal loads all year round. It is vital to select the right facade system, with careful consideration of the balance between solar shading property and thermal insulation property, taking the region and orientation into account.
Solar shading property is high = Low cooling load and high heating load[Figure 1-(A)]
Thermal insulation property is high = High cooling load and low heating load[Figure 2-(C)]
Thermal property of facade and interior comfort
For occupants of the building interior, comfort is important, not just energy saving. To secure comfort in the perimeter zone close to the facade, the temperature of the interior surface of the facade must be maintained at an appropriate level.
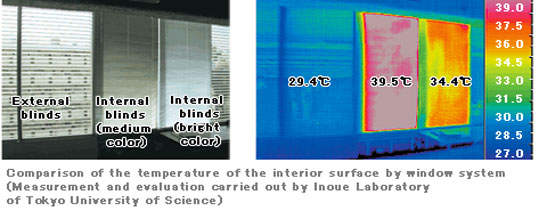
*A facade with superior solar shading and thermal insulation property mitigates the impact of the changing exterior environment, reducing changing in the interior surface temperature of the facade to maintain comfort in the interior. Selection of the right facade system is also important for interior comfort as an assessment indicator.
Summer & Intermediate Season
When the solar heat raise the temperature of the interior surface. → Room is maintained at an appropriate level but occupants around window feel hot.
Winter
When nighttime and cloudy weather fall the temperature of the interior surface. → Room is maintained at an appropriate level but occupants around window feel cold.
*A facade with superior solar shading and thermal insulation property mitigates the impact of the changing exterior environment, reducing changing in the interior surface temperature of the facade to maintain comfort in the interior. Selection of the right facade system is also important for interior comfort as an assessment indicator.